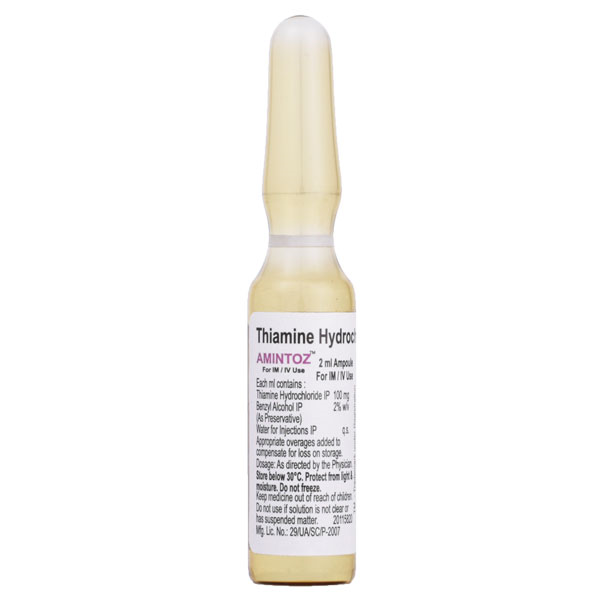
Product Introduction:
Amintoz Injection is a pharmaceutical product containing Thiamine (Vitamin B1) in a concentration of 100mg per injection. Thiamine is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including energy metabolism and nerve function.
Amintoz Injection is given under the supervision of a healthcare professional and should not be self-administered. You should take it regularly to get the most benefit from it. This medicine may be only part of a complete program of treatment that also includes making changes to your diet and taking calcium and vitamin supplements.
Amintoz Injection may cause some common side effects such as injection site reactions, skin irritations, cough, and decreased blood pressure. Before taking this medicine, let your doctor know if you have any heart, kidney, or liver disease. Some other medicines can decrease the absorption of vitamins so let your doctor know all other medicines you are taking to make sure you are safe. It is important to ask your doctor’s advice before taking any other vitamin supplements.
Benefits:
- Energy Production: Thiamine helps convert carbohydrates into energy, supporting overall energy levels.
- Nervous System Health: It plays a vital role in maintaining the health of the nervous system, including the proper functioning of nerves.
- Metabolic Support: Thiamine is involved in the metabolism of proteins and fats, aiding in overall metabolic processes.
- Cardiovascular Health: It may contribute to the maintenance of a healthy cardiovascular system.
Side Effects:
While Thiamine is generally considered safe when taken in appropriate doses, some individuals may experience side effects, including:
- Allergic Reactions: Some people may experience allergic reactions such as itching, rash, or difficulty breathing.
- Injection Site Reactions: Pain, redness, or swelling at the injection site may occur.
- Digestive Upset: High doses of Thiamine may cause digestive upset, including nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea.
Usage Guidelines:
Amintoz Injection should be administered under the supervision of a healthcare professional, typically by intramuscular or intravenous injection. The dosage and frequency of administration will depend on the individual’s condition and medical history. It is essential to follow the instructions provided by the healthcare provider or the product label carefully. Do not exceed the recommended dosage without consulting a healthcare professional.
Drug Interactions:
Thiamine may interact with certain medications or substances. Some potential interactions include:
- Diuretics: Certain diuretic medications may increase the excretion of Thiamine from the body, potentially leading to Thiamine deficiency.
- Alcohol: Chronic alcohol consumption can interfere with Thiamine absorption and utilization, leading to Thiamine deficiency.
- Antacids: Some antacid medications may decrease Thiamine absorption from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Medications for Seizures: Certain anticonvulsant medications may reduce Thiamine levels in the body.
It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, or herbal products you are taking before starting Thiamine supplementation to avoid potential interactions.
Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new medication or supplement regimen, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions or are taking other medications.
SAFETY ADVICE

Alcohol

Pregnancy
Breast feeding

Driving

Kidney

Liver
| Weight | 0.5 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 10 × 10 × 10 cm |