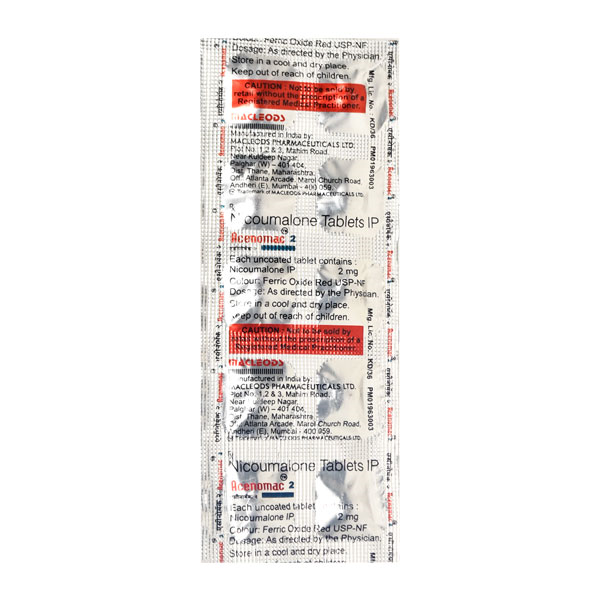
ACENOMAC 2MG TABLET
KEY BENIFITS,
- Anticoagulation: Acenocoumarol inhibits the synthesis of certain clotting factors in the liver, preventing the formation of blood clots.
- Thrombosis Prevention: Used to prevent and treat conditions associated with abnormal blood clotting, reducing the risk of thrombosis.
- Maintaining Blood Flow: Helps maintain blood flow in conditions like atrial fibrillation and after heart valve surgery.
₹108.90
Compare- Introduction:
- Acenomac 2mg Tablet contains the anticoagulant (blood thinner) Acenocoumarol. It is used to prevent and treat conditions where blood clotting needs to be controlled, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), pulmonary embolism, and certain heart conditions.
Acenomac 2mg Tablet should be taken as advised by the doctor. You may take it with or without food but it is better to take it at a fixed time. This medicine should not be stopped abruptly without consulting the doctor. You should take this medicine regularly to get the most benefit, even if you feel fine. It is preventing future harm.
Use of this medicine may increase your risk of bleeding. Let your doctor know immediately if you see a pinpoint rash or blood in your vomits, urine, or stool. If you are going under any surgery or dental treatment, you may need to stop this medicine for some time but only after consulting with your doctor.
Before taking it, you must inform the doctor if you are suffering from any kidney or liver disease. Also, let your doctor know if you are pregnant or breastfeeding and about all the other medications that you are taking regularly.
- Benefits:
- Anticoagulation: Acenocoumarol inhibits the synthesis of certain clotting factors in the liver, preventing the formation of blood clots.
- Thrombosis Prevention: Used to prevent and treat conditions associated with abnormal blood clotting, reducing the risk of thrombosis.
- Maintaining Blood Flow: Helps maintain blood flow in conditions like atrial fibrillation and after heart valve surgery.
- Side Effects:
- Bleeding: The most significant side effect is an increased risk of bleeding. It can manifest as nosebleeds, bleeding gums, easy bruising, or prolonged bleeding from cuts.
- Hematoma Formation: Accumulation of blood in tissues leading to a lump or swelling.
- Skin Necrosis: Rarely, skin necrosis can occur at the injection site.
- Drug Interactions:
- Interactions with Other Anticoagulants: Increased risk of bleeding when combined with other anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs.
- Interaction with NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can enhance the anticoagulant effect, leading to an increased risk of bleeding.
- Certain Antibiotics: Some antibiotics may interact with Acenocoumarol and affect its effectiveness.
- Dosage and Administration:
- The dosage is individualized based on the patient’s specific medical condition and response to treatment.
- Regular monitoring of international normalized ratio (INR) is essential to ensure the medication’s effectiveness and prevent bleeding complications.
- Special Precautions and Warnings:
- Risk of Bleeding: Due to the anticoagulant effect, there is an increased risk of bleeding. Caution is needed, especially in patients with a history of bleeding disorders.
- Regular Monitoring: INR levels need to be monitored regularly to ensure the drug’s effectiveness and prevent complications.
- Interaction with Foods: Vitamin K-rich foods can interfere with the anticoagulant effect, so a consistent intake of vitamin K-containing foods is advised.
- Advisory:
- Always inform healthcare providers about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs and herbal supplements.
- Report any signs of bleeding or unusual bruising promptly.
- Follow healthcare provider recommendations regarding diet and lifestyle modifications.
Acenomac 2mg Tablet should only be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional who can provide specific information about the product, its formulation, and any precautions or considerations based on the patient’s health status.
SAFETY ADVICE

Alcohol

Pregnancy
Breast feeding

Driving

Kidney
Use of Acenomac 2mg Tablet is not recommended in patients with severe kidney disease.

Liver
Use of Acenomac 2mg Tablet is not recommended in patients with severe liver disease.
| Weight | 0.5 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 10 × 10 × 10 cm |