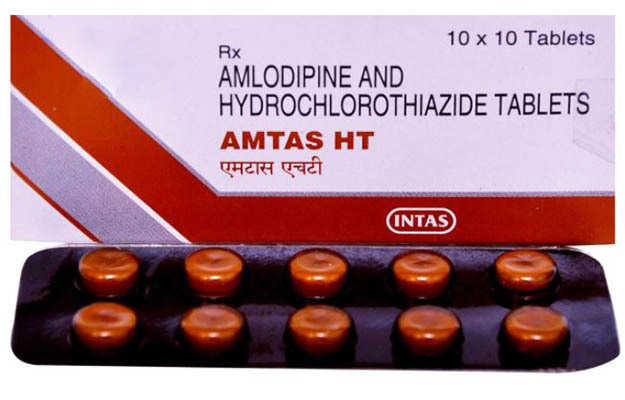
Product Introduction:
Amtas HT tablet is a pharmaceutical product that combines two active ingredients: Amlodipine (5mg) and Hydrochlorothiazide (12.5mg). This combination medication is primarily prescribed for the management of hypertension (high blood pressure). Amlodipine is a calcium channel blocker, while Hydrochlorothiazide is a thiazide diuretic. Together, they work to widen blood vessels and reduce fluid retention, thereby lowering blood pressure.
Amtas HT Tablet is a combination medicine used in the treatment of hypertension (high blood pressure). It also helps to reduce the risk of stroke and heart attack. This medicine should be used along with a proper diet, salt restriction, and regular exercise for best results. It should be taken with or without food preferably in the morning, to avoid frequent urination at night. This medicine may cause dehydration, so it is better to take plenty of fluids. Inform doctor if you develop extreme thirst and muscle weakness. Some patients may develop swelling of ankle as a side effect of using this medicine.
Benefits:
- Blood Pressure Control: Amtas HT tablet effectively lowers elevated blood pressure, reducing the risk of cardiovascular events such as heart attacks and strokes.
- Combination Therapy: The combination of Amlodipine and Hydrochlorothiazide offers synergistic effects, providing enhanced blood pressure-lowering benefits compared to either drug alone.
- Fluid Retention Reduction: Hydrochlorothiazide helps to reduce fluid retention by increasing urine production, which can be particularly beneficial for patients with hypertension associated with edema or fluid overload.
Side Effects:
Common side effects of Amtas HT tablet may include:
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Fatigue
- Hypokalemia (low potassium levels)
- Increased urination
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Muscle cramps
- Nausea
- Photosensitivity
Rare but serious side effects may include:
- Allergic reactions
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Hyperkalemia (high potassium levels)
- Kidney dysfunction
- Liver toxicity
Usage Guidelines:
- Dosage: The usual dose is one tablet daily, or as directed by a healthcare provider.
- Administration: Amtas HT tablet should be taken orally with or without food.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular blood pressure monitoring is recommended to ensure the medication is effectively controlling blood pressure.
- Do Not Stop Abruptly: Discontinuing Amtas HT suddenly may lead to rebound hypertension. Consult a doctor before stopping the medication.
Drug Interactions:
- Potassium-Sparing Diuretics: Concomitant use with potassium-sparing diuretics may increase the risk of hyperkalemia (high potassium levels).
- Other Antihypertensive Medications: Concurrent use with other blood pressure-lowering drugs may potentiate the hypotensive effects of Amtas HT.
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may reduce the antihypertensive effects of Amtas HT and increase the risk of kidney damage.
- Lithium: Amtas HT may increase lithium levels, leading to toxicity.
Precautions:
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Amtas HT is not recommended during pregnancy or breastfeeding due to potential harm to the fetus or infant. Alternative therapies should be considered.
- Renal Impairment: Caution is advised in patients with renal impairment, as Amtas HT may exacerbate kidney dysfunction.
- Hepatic Impairment: Use with caution in patients with liver impairment, as Amtas HT metabolism may be affected.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Patients at risk of electrolyte imbalances, such as those with kidney problems or on potassium supplements, should be closely monitored.
Always consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice regarding the use of Amtas HT tablet, including dosage adjustments, potential drug interactions, and management of side effects.
SAFETY ADVICE

Alcohol

Pregnancy
Breast feeding

Driving
Amtas HT Tablet may cause side effects such as dizziness, headaches, nausea or tiredness, all of which could affect your ability to concentrate and drive.

Kidney
Use of Amtas HT Tablet is not recommended in patients with severe kidney disease.

Liver
| Weight | 0.5 kg |
|---|---|
| Dimensions | 10 × 10 × 10 cm |